Data & Analytics
Verizon DBIR 2016: Web Application Attacks are the No. 1 Source of Data Breaches (HITS)
Story Highlights
Verizon recently released its Data Breach Investigation Report (DBIR) for 2016. The DBIR is based on real-world investigations and reports of over 100,000 security incidents. It examines trends across different industry verticals such as finance, retail, information technology and others. One of the most startling findings in this year’s report is the disproportionate number of web application attacks that result in a data breach. Although attacks on web applications account for only 8 percent of overall reported incidents (whether they were successful or not), attacks on web applications accounted for over 40 percent of incidents resulting in a data breach, and were the single-biggest source of data loss.
The report also revealed that the volume of data breaches caused by web application attacks is rapidly rising: the percentage of data breaches that leveraged web application attacks has increased rapidly in the last year – from only about 7 percent in 2015 to 40 percent. These findings are a clear indication that web applications in many organizations are not just exposed, but are disproportionately vulnerable compared to other points of attack.
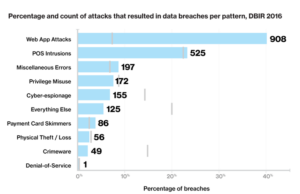
The graph below shows the incidence rates of different attack methods that resulted in a loss of data. The gray bars indicate the corresponding figure from the DBIR report for 2015. The graph clearly illustrates that web application attacks accounted for the greatest percentage of attacks that resulted in breaches, an increase of almost fivefold from 2015:
With these findings in mind, the DBIR recommends that businesses implement a number of security measures such as multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to web applications, anti-malware security measures, extensive validation of web application user inputs and suggests establishing a patching process for their content management systems (CMS) and third-party plugins.
Following through on these recommendations, there are a number of measures for organizations to think about when considering how to best protect themselves from a data breach:
– Implement a Web Application Firewall (WAF): A WAF can help prevent several popular types of attacks, such as SQL injection, cross-site-scripting and others that leverage issues in web application input validation and vulnerabilities in systems running web applications to cause data breaches.
– Customize your security profile: No two websites are alike, and different web applications work in different ways, leading to a different threat profile. As a result, it is imperative for each website to customize security measures to suit its specific requirements and needs.
– Protect your CMS: Content management and publication software, such as Drupal, WordPress, Joomla and others are an increasing source of vulnerability used in many incidents. A solution that provides automatic, zero-day protection, known as”‘virtual patching”, for common CMS software will help you protect yourself against such vulnerabilities.
– Block known bad actors: Many attacks today are mounted via globally distributed bot networks run by criminal rings. Using a solution that includes a built-in IP reputation database enables you to automatically block bad actors before they ever reach your network.
– Integrate with other security measures: Finally, keep in mind that protecting your web applications is just one aspect of securing your overall online presence. Other layers of security include protection against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, protection for your Domain Name System (DNS), and content encryption with SSL/TLS. When considering a WAF, make sure you choose one that can give you comprehensive, multi-layer protection.









